Mr Ravi Balakrishnan spoke on Communication, efficiency, reach, decision making and networking. Communication includes handling an organization using technology efficiently- email, social media, VOIP. Efficiency refers to streamlining operation, task automation, data management and analytics using tech. Reach refers to expanding reach to local communities. Decision making refers to data driven decision making, data analytics, improved program information and services. Getting data can be legally binding and exhausting. Not all data cannot be trusted as they can be manipulated. CSOs should collaborate with other organizations, social media groups and engage in corporate events.
Anand Rangachari discussed how technology plays a critical role in healthcare for rural communities and has a major role in grassroots. Healthcare has shifted as an industry: health, wellness, safety. The Government has changed to managing diseases and conducting physical exams on our own for prevention and diagnosis.
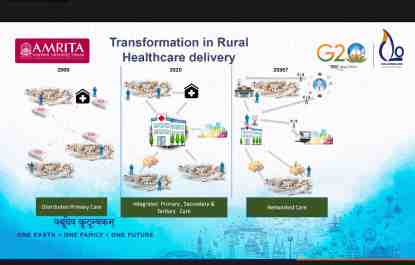
In the past, safety took a backseat but these days the healthy also want to know their genetic predilections and focus on wellness. Gamut of healthcare services has evolved. The evolution is from distributed primary care to integrated primary, secondary and tertiary care to now networked care. Awareness of preventive health has increased. Increasing life expectancy all over the world. Technology is helping consumer demand for free, perfect quality, and instant services. Recommendations for easy access to medical services for rural areas: chatgpt might be the solution. Hospitals should be able to corroborate information. Remote areas aren’t really remote anymore. No villages are inaccessible by road. Chatgpt could assist doctors to get patient history and facilitate treatment. Innovative tech management can help issues faced by underprivileged people. However, they do not have the luxury to perform experiments with technology as the stakes are too high.
Tech tools are constantly evolving. CSOs have to get a feel of the tools but may choose not to use all aspects of it. They could focus on what is useful to them. There is a need to obtain subsidies for technology licenses. Getting funding for tech for NGOs and CSOs may not be easy as donors psychologically do not feel they are having a direct impact when they donate for technology as opposed to other things. Further, technology expenses aren’t too transparent in terms of billing etc.
Unemployment should not be affected by technology as it actually includes people than before. Roles may become obsolete but people cannot be. As per skills, they could find jobs. Unless technology creates employment, unemployment is not possible.
Product market is controlled by a middle man. Indian NGOs are choosing to adopt certain things but not others. Like Gpay. Product sales are not thinking about safety or security of information yet. People don’t trust the technology; they trust that others are using it and it works.